brainpy.math.surrogate.leaky_relu#
- brainpy.math.surrogate.leaky_relu(x, alpha=0.1, beta=1.0)[source]#
Judge spiking state with the Leaky ReLU function.
If origin=False, computes the forward function:
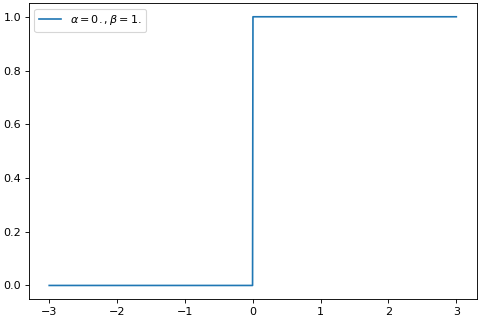
\[\begin{split}g(x) = \begin{cases} 1, & x \geq 0 \\ 0, & x < 0 \\ \end{cases}\end{split}\]If origin=True, computes the original function:
\[\begin{split}\begin{split}g(x) = \begin{cases} \beta \cdot x, & x \geq 0 \\ \alpha \cdot x, & x < 0 \\ \end{cases}\end{split}\end{split}\]Backward function:
\[\begin{split}\begin{split}g'(x) = \begin{cases} \beta, & x \geq 0 \\ \alpha, & x < 0 \\ \end{cases}\end{split}\end{split}\]>>> import brainpy as bp >>> import brainpy.math as bm >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> xs = bm.linspace(-3, 3, 1000) >>> bp.visualize.get_figure(1, 1, 4, 6) >>> grads = bm.vector_grad(bm.surrogate.leaky_relu)(xs, 0., 1.) >>> plt.plot(bm.as_numpy(xs), bm.as_numpy(grads), label=r'$\alpha=0., \beta=1.$') >>> plt.legend() >>> plt.show()
(
Source code,png,hires.png,pdf)