Training with Online Algorithms#
import brainpy as bp
import brainpy.math as bm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import brainpy_datasets as bd
bm.set_environment(x64=True, mode=bm.batching_mode)
bm.set_platform('cpu')
bp.__version__
'2.4.0'
Online training algorithms, such as FORCE learning, have played vital roles in brain modeling. BrainPy provides brainpy.train.OnlineTrainer for model training with online algorithms.
Train a reservoir model#
Here, we are going to use brainpy.OnlineTrainer to train a next generation reservoir computing model (NGRC) to predict chaotic dynamics.
We first get the training dataset.
def get_subset(data, start, end):
res = {'x': data.xs[start: end],
'y': data.ys[start: end],
'z': data.zs[start: end]}
res = bm.hstack([res['x'], res['y'], res['z']])
# Training data must have batch size, here the batch is 1
return res.reshape((1, ) + res.shape)
dt = 0.01
t_warmup, t_train, t_test = 5., 100., 50. # ms
num_warmup, num_train, num_test = int(t_warmup/dt), int(t_train/dt), int(t_test/dt)
lorenz_series = bd.chaos.LorenzEq(t_warmup + t_train + t_test,
dt=dt,
inits={'x': 17.67715816276679,
'y': 12.931379185960404,
'z': 43.91404334248268})
X_warmup = get_subset(lorenz_series, 0, num_warmup - 5)
X_train = get_subset(lorenz_series, num_warmup - 5, num_warmup + num_train - 5)
X_test = get_subset(lorenz_series,
num_warmup + num_train - 5,
num_warmup + num_train + num_test - 5)
# out target data is the activity ahead of 5 time steps
Y_train = get_subset(lorenz_series, num_warmup, num_warmup + num_train)
Y_test = get_subset(lorenz_series,
num_warmup + num_train,
num_warmup + num_train + num_test)
Then, we try to build a NGRC model to predict the chaotic dynamics ahead of five time steps.
class NGRC(bp.DynamicalSystemNS):
def __init__(self, num_in):
super(NGRC, self).__init__()
self.r = bp.layers.NVAR(num_in, delay=2, order=2, constant=True)
self.o = bp.layers.Dense(self.r.num_out, num_in, b_initializer=None, mode=bm.training_mode)
def update(self, x):
return x >> self.r >> self.o
model = NGRC(3)
model.reset(1)
Here, we use ridge regression as the training algorithm to train the chaotic model.
trainer = bp.OnlineTrainer(model, fit_method=bp.algorithms.RLS(), dt=dt)
# first warmup the reservoir
_ = trainer.predict(X_warmup)
# then fit the reservoir model
_ = trainer.fit([X_train, Y_train])
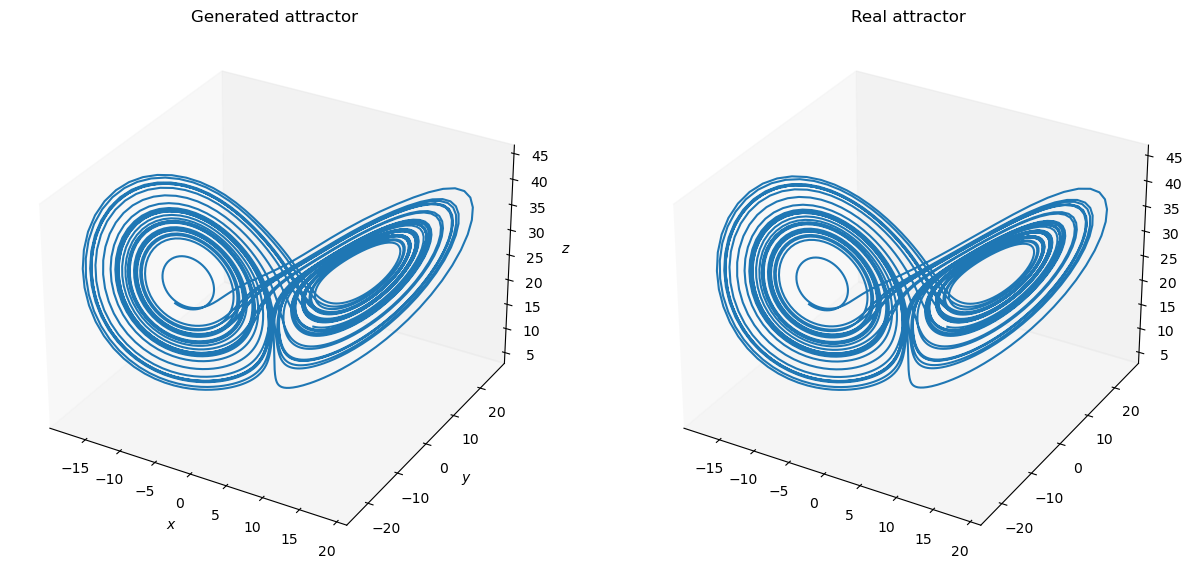
def plot_lorenz(ground_truth, predictions):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(121, projection='3d')
ax.set_title("Generated attractor")
ax.set_xlabel("$x$")
ax.set_ylabel("$y$")
ax.set_zlabel("$z$")
ax.grid(False)
ax.plot(predictions[:, 0], predictions[:, 1], predictions[:, 2])
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122, projection='3d')
ax2.set_title("Real attractor")
ax2.grid(False)
ax2.plot(ground_truth[:, 0], ground_truth[:, 1], ground_truth[:, 2])
plt.show()
# finally, predict the model with the test data
outputs = trainer.predict(X_test)
print('Prediction NMS: ', bp.losses.mean_squared_error(outputs, Y_test))
plot_lorenz(bm.as_numpy(Y_test).squeeze(), bm.as_numpy(outputs).squeeze())
Prediction NMS: 0.0008616580175702455