brainpy.math.surrogate.multi_gaussian_grad#
- brainpy.math.surrogate.multi_gaussian_grad(x, h=0.15, s=6.0, sigma=0.5, scale=0.5)[source]#
Spike function with the multi-Gaussian gradient function [1].
The forward function:
\[\begin{split}g(x) = \begin{cases} 1, & x \geq 0 \\ 0, & x < 0 \\ \end{cases}\end{split}\]Backward function:
\[\begin{array}{l} g'(x)=(1+h){{{\mathcal{N}}}}(x, 0, {\sigma }^{2}) -h{{{\mathcal{N}}}}(x, \sigma,{(s\sigma )}^{2})- h{{{\mathcal{N}}}}(x, -\sigma ,{(s\sigma )}^{2}) \end{array}\]>>> import brainpy as bp >>> import brainpy.math as bm >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> xs = bm.linspace(-3, 3, 1000) >>> bp.visualize.get_figure(1, 1, 4, 6) >>> grads = bm.vector_grad(bm.surrogate.multi_gaussian_grad)(xs) >>> plt.plot(bm.as_numpy(xs), bm.as_numpy(grads)) >>> plt.show()
(
Source code,png,hires.png,pdf)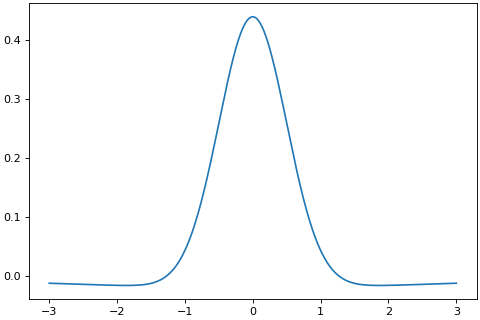
- Parameters:
- Returns:
out – The spiking state.
- Return type:
jax.Array
References
